Microscopy Sources
Light Conversion’s product portfolio features microscopy-dedicated femtosecond laser sources CRONUS-2P and CRONUS-3P.
These lasers cover applications in functional neuroimaging, optogenetics, and deep imaging using medium-repetition-rate three-photon excitation and fast high‑repetition-rate two-photon imaging, as well as widefield and holographic excitation using high-power laser sources. See the comparison table for the CRONUS series below. For a complete list of laser sources available for nonlinear microscopy and examples of state-of-the-art applications, please refer to the latest brochure.
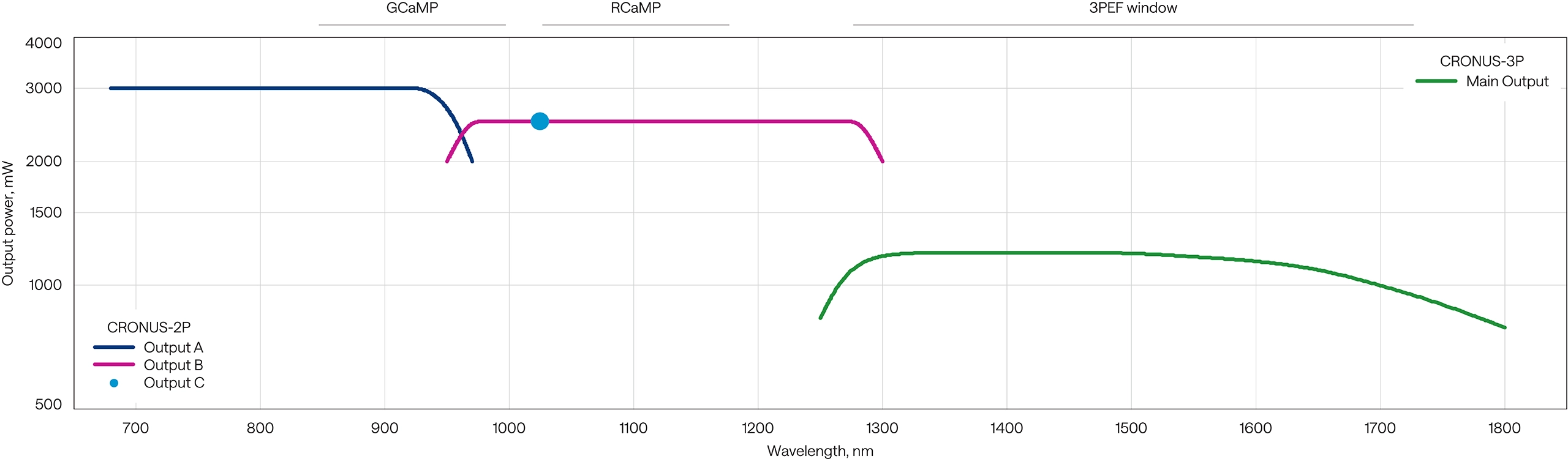
| Product | Outputs | Output power | Repetition rate | Pulse duration |
|---|
- Up to three simultaneous and synchronized outputs for multibeam excitation. For a fixed-wavelength laser, refer to FLINT.
- For dual output, refer to ORPHEUS-TWINS in ORPHEUS-F configuration.
- An alternative configuration with an additional 920 nm output is available, contact sales@lightcon.com.
- At 1 MHz repetition rate. Lower repetition rate and higher pulse energy options are available.
- Expressed as normalized root mean squared deviation (NRMSD).
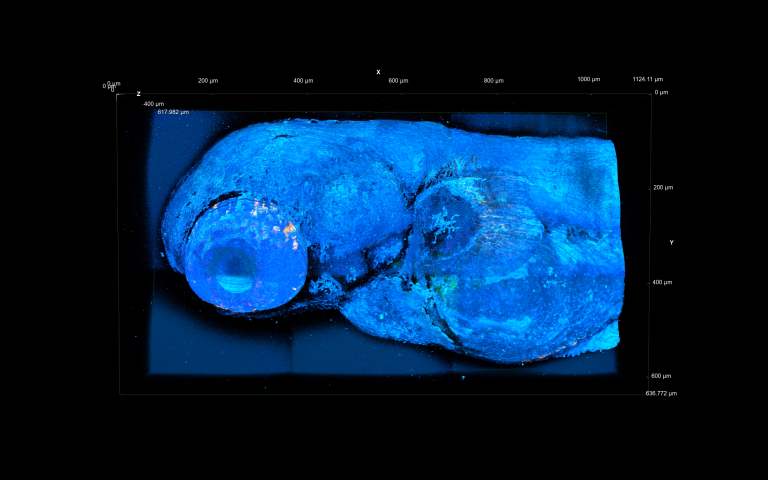
Multimodal 3D imaging of a live zebrafish at 1300 nm 3P excitation using CRONUS-3P.
3PEF – green, trans SHG – yellow, epi THG – dark blue,
trans THG – cyan.
Courtesy of Luigi Bonacina group, University of Geneva.
Multimodal 3D imaging of a live zebrafish at 1300 nm 3P excitation using CRONUS-3P.
3PEF – green, trans SHG – yellow, epi THG – dark blue,
trans THG – cyan.
Courtesy of Luigi Bonacina group, University of Geneva (2024).

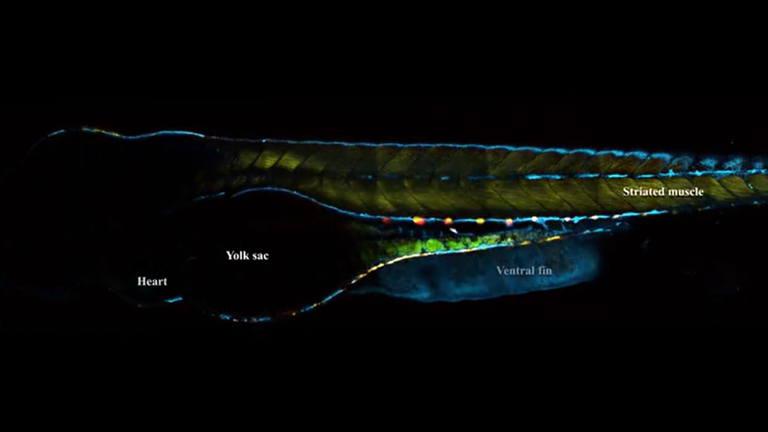
Multimodal 3D imaging of a live zebrafish yolk sac at 1300 nm 3P excitation using CRONUS-3P.
3PEF – green, transmitted THG – white.
Courtesy of Luigi Bonacina group, University of Geneva (2024).
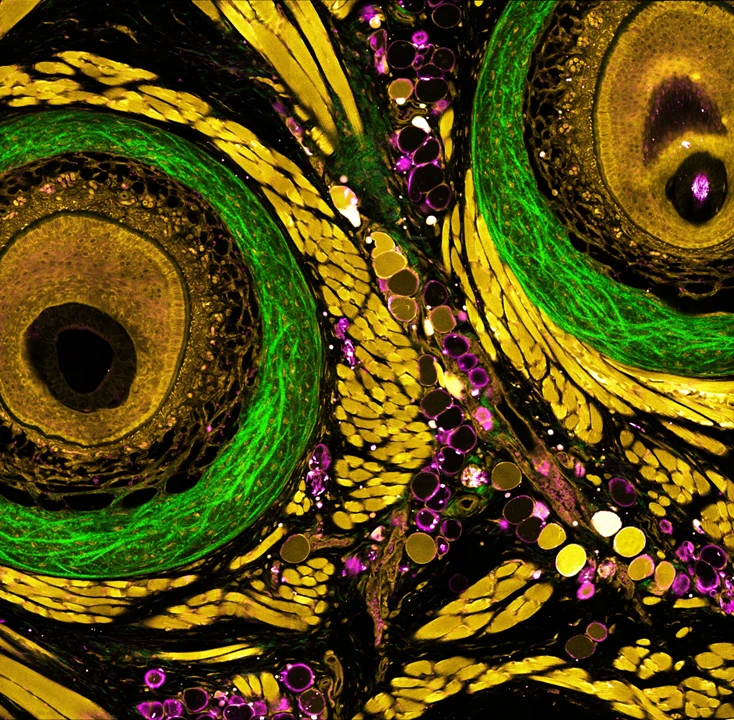
The microenvironment of an intact mouse whisker pad, revealed through multiplex label-free nonlinear microscopy using CRONUS-3P, illuminated at 1300 nm.
Courtesy of Kunzan Liu, Sixian You laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
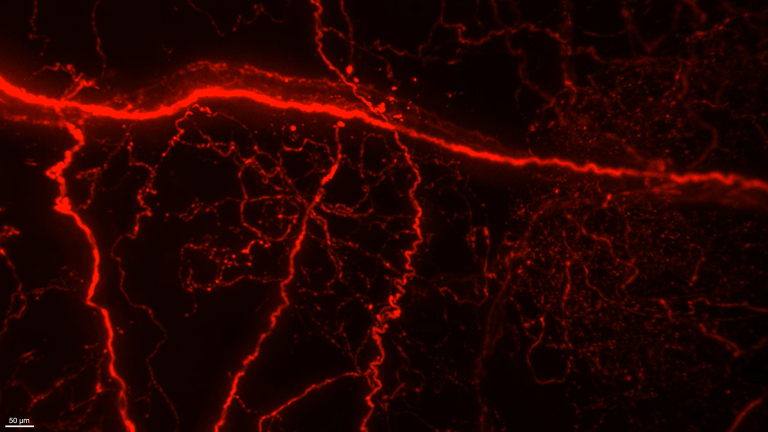
2P light-sheet imaging of the atrium in an adult mouse, acquired using the CARBIDE femtosecond laser with I-OPA.
Courtesy of Bliq Photonics.
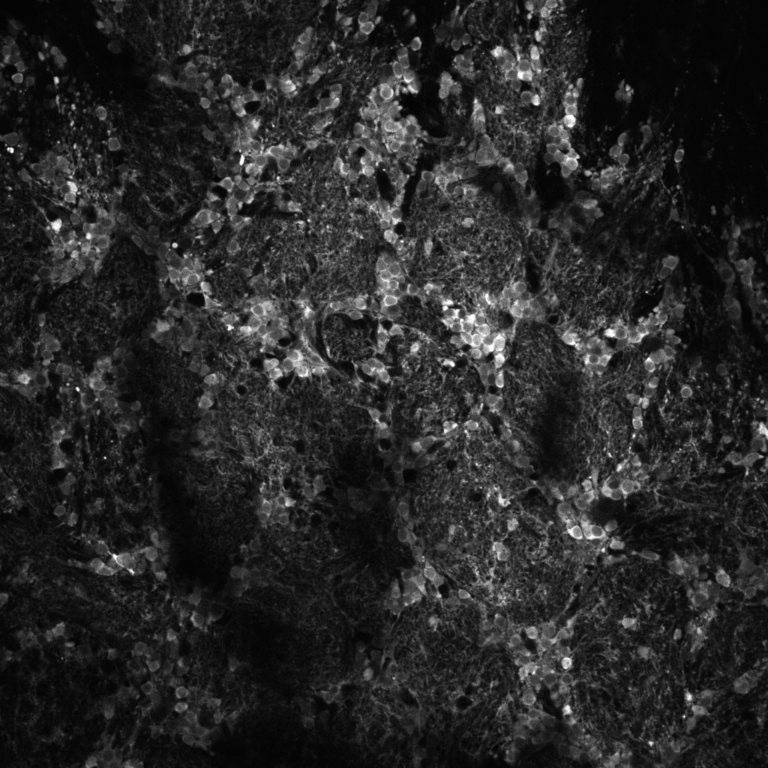
Mouse olfactory bulb with inhibitory cells labelled with GCaMP8s. Anatomical Z-stack imaged in 3P at 1300 nm down to 650 µm, 20 µm per step.
Source: Fred Marbach, Andreas Schaefer lab, The Francis Crick Institute, unpublished 2025 data.

Functional three-photon neuroimaging of a zebrafish using an OEM OPA in the ORPHEUS-F configuration.
Courtesy of Chris Xu and Joseph R. Fetcho groups, Cornell University.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-020-0819-7
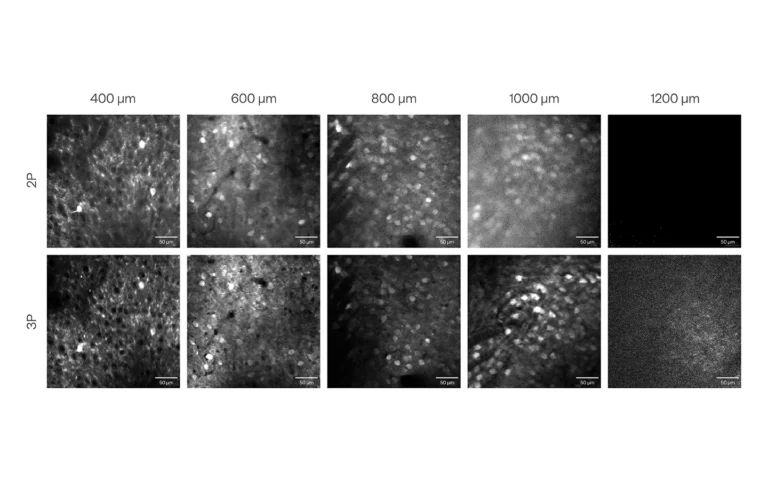
Comparison of in vivo 2P and 3P calcium imaging of mouse visual cortex GCaMP neurons on a Thorlabs Bergamo II microscope using typical 2P laser and Light Conversion CRONUS-3P (3P) laser at 920 nm and 1300 nm, respectively.
Courtesy of CSHL ISFNS 2024 school organizers and Willis Broden Jr. and Sergey Matveev (Thorlabs).
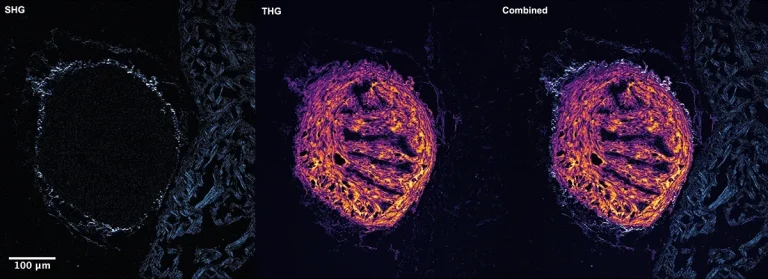
Adult zebrafish heart ventricle section, imaged using the FLINT femtosecond oscillator.
Samples courtesy of Justas Lazutka at the Vilnius University Life Sciences Center. Nonlinear imaging courtesy of the Barzda group at the Vilnius University Department of Physics.
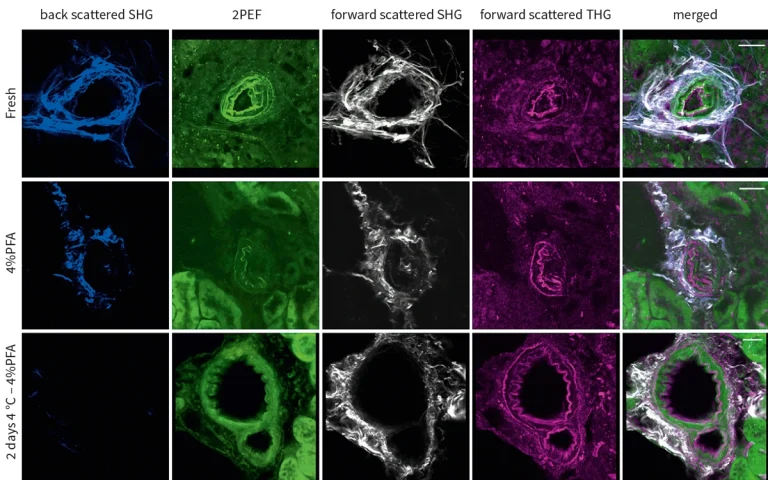
SHG signals from collagen, 2PEF, and THG signals from elastin in vibratome sections of mouse kidney after different treatments, acquired using CRONUS-2P.
Courtesy of Frauke Alves and Fernanda Ramos-Gomes, Max-Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences, Germany.
DOI: 10.1364/BOE.488453
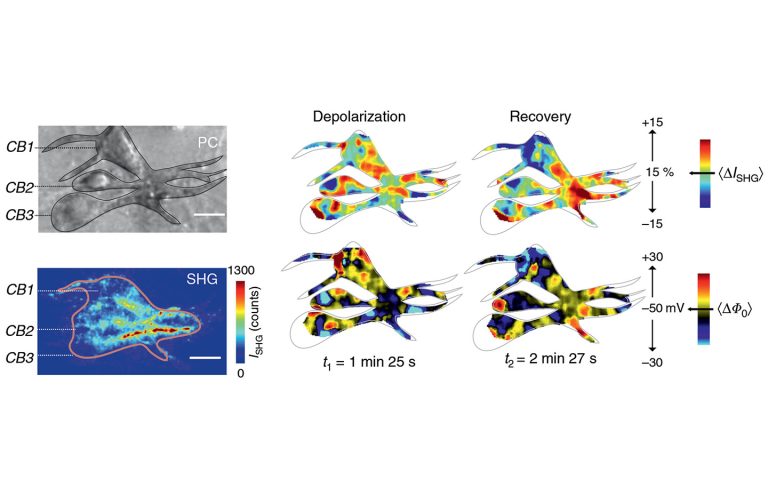
Widefield SHG neuroimaging of neuronal membrane potentials and ion efflux by means of water, acquired using the PHAROS femtosecond laser.
Courtesy of Sylvie Roke group, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07713-w
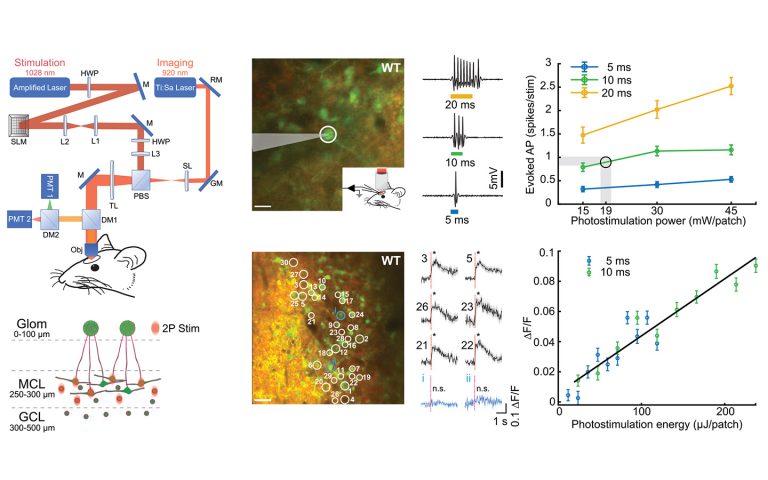
Holographic 2P optogenetic stimulation of mouse olfactory bulb neurons using the PHAROS femtosecond laser.
Courtesy of Shy Shoham and Dmitry Rinberg groups, New York University.
DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.07.034
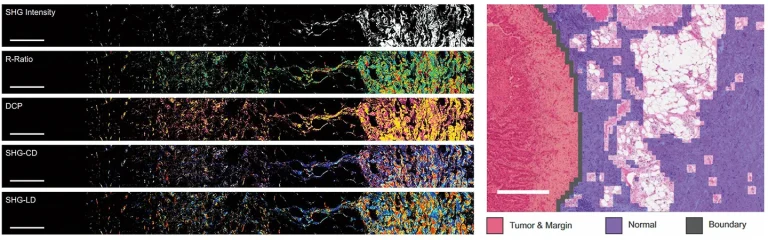
Large-area wide-field polarization-resolved SHG microscopy of a human lung tissue tumor margin using the PHAROS femtosecond laser.
Courtesy of Virginijus Barzda group, University of Toronto, and Brian C. Wilson group, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24973-1
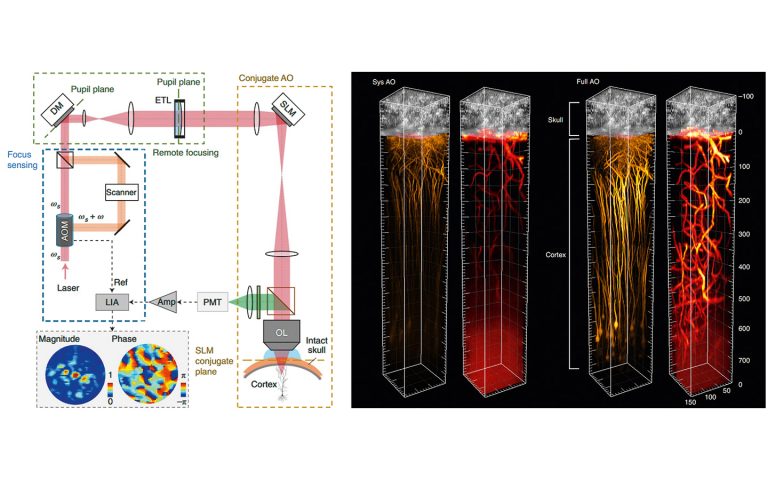
3P microscopy with adaptive optics for focus sensing and shaping to compensate for both aberrations and scattering. ORPHEUS-F excitation at 1300 nm enabled imaging up to 1.1 mm below the pia within the intact brain.
Courtesy of Jianan Y. Qu group, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01343-w
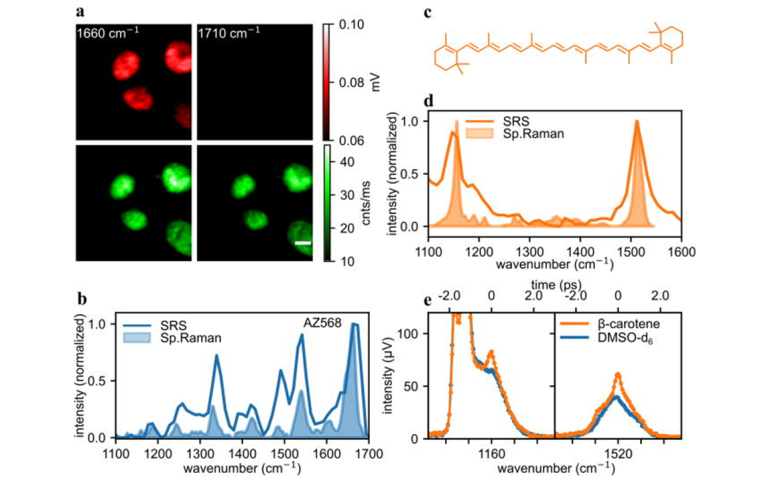
(a) Imaging of nuclei of AZ568 stained, fixed HeLa cells with SRS (red) and fluorescence (green). (b) SRS and spontaneous Raman spectrum (at 488 nm) of 1 mM solution of AZ568 in DMSO-d6. (c) Structure of β-carotene. (d) β-Carotene spectrum recorded with SRS and spontaneous Raman. (e) Spectral focusing spectrum of β-carotene solution in DMSO-d6. The images were recorded using CRONUS-2P.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0171725
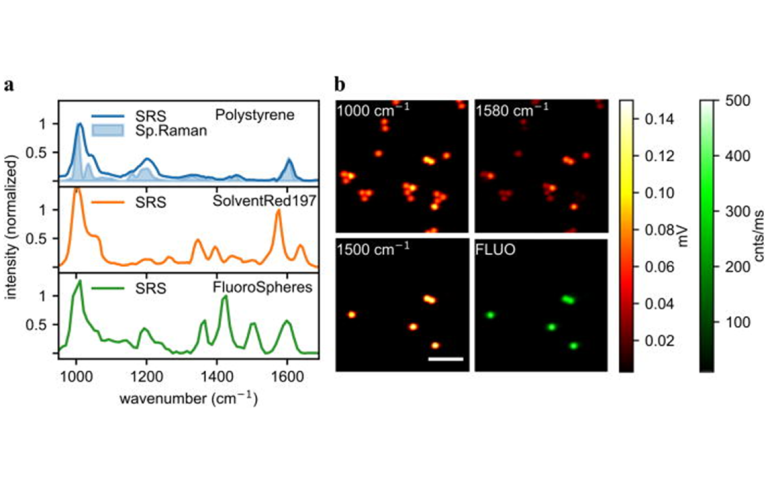
(a) Spontaneous Raman and SRS spectra of polymeric materials, normalized with the molecule of interest maximum peak. (b) SRS images of dyed and un-dyed PS beads. Images were recorded using CRONUS-2P.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0171725
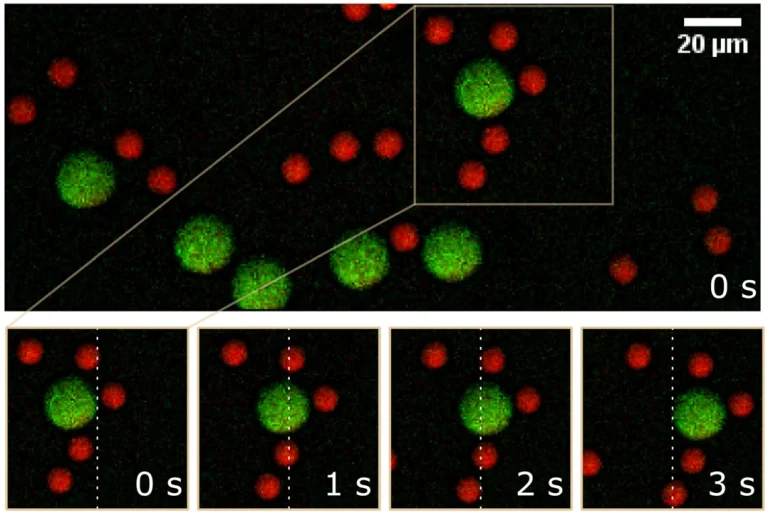
CARS images of flowing PS and PMMA beads, acquired using CRONUS-2P. The bottom images show a time course of a selected area as indicated with 1 s intervals to exemplify the flow. The white dashed line is for motion reference.
DOI: 10.1002/jrs.6671
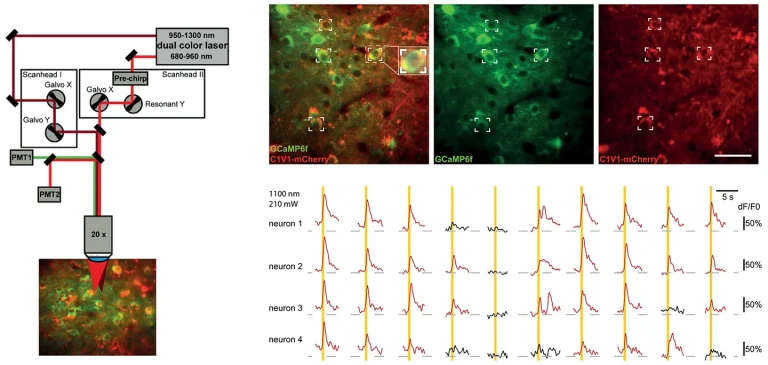
2P optogenetic stimulation of individual neurons using CRONUS-2P.
Courtesy of Albrecht Stroh group, University Medical Center Mainz and Leibniz Institute for Resilience Research.
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102184
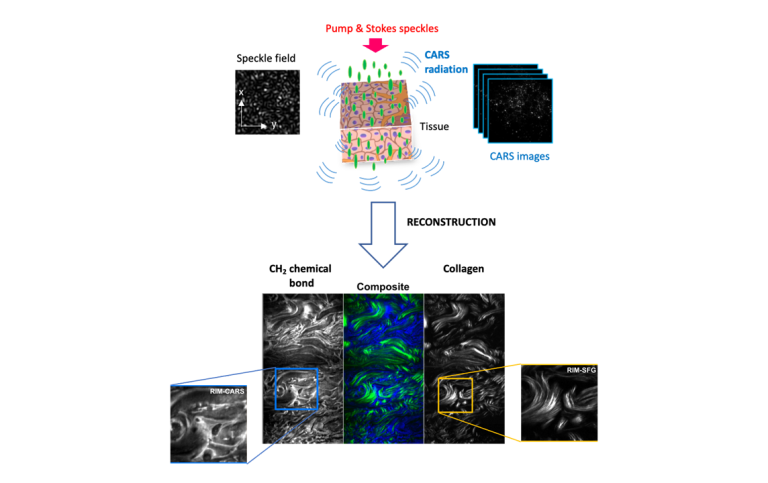
RIM-CARS and RIM-SFG imaging of molecular chemical bonds with a wide-field camera, using PHAROS and ORPHEUS-HP.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-023-01294-x
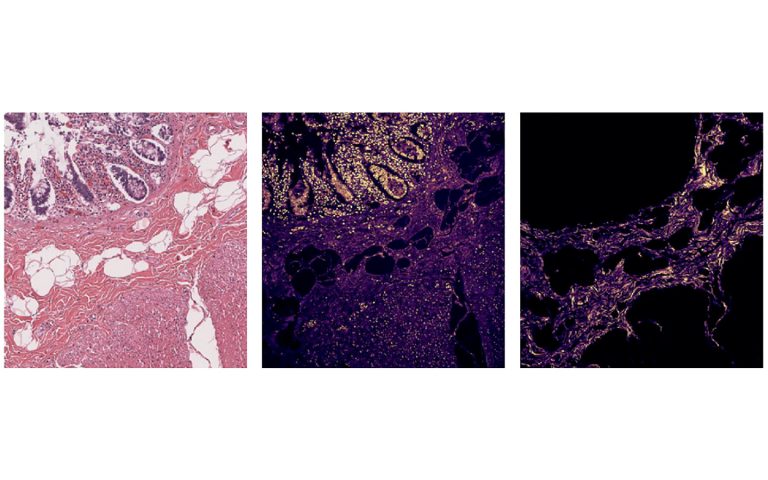
SHG and THG images of H&E-stained colon using the FLINT femtosecond oscillator.
Courtesy of Virgis Barzda group, Vilnius University.
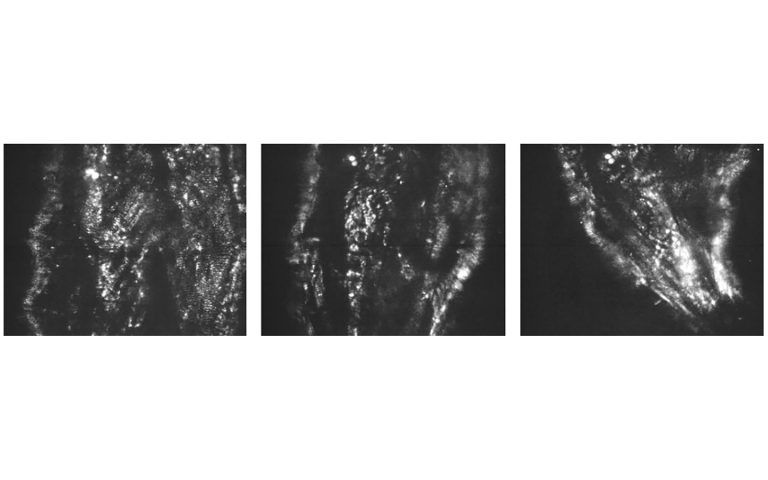
Label-free in vivo widefield SHG imaging of a fruit fly larva using the PHAROS femtosecond laser.
Courtesy of Virgis Barzda group, University of Toronto.
Application examples
Product catalog
Product catalog
Product catalog in Chinese